Diet High in Nuts, Beans, and Tofu Linked to 20% Lower Risk of Brain-Damaging Diseases, Scientists Report
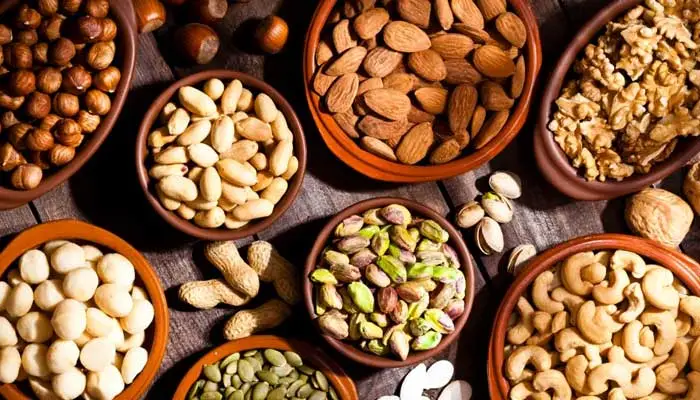
In a groundbreaking study, American scientists have found that consuming a diet rich in nuts, beans, and tofu can significantly reduce the risk of developing brain-damaging diseases by 20 percent. This research highlights the protective benefits of these foods, which are particularly effective in lowering these risks due to their high content of essential nutrients and antioxidants.
Dried fruits, beans, and tofu, a cheese-like product made from soybeans, have been identified as key components in reducing the likelihood of developing neurological conditions. The study emphasizes the importance of incorporating these foods into one’s diet to promote brain health and prevent diseases.
Conversely, the study sheds light on the detrimental effects of processed red meat. Nitrates and other chemicals used in preserving these meats not only increase the risk of cancer but also have been found to damage the brain. Yuha Lee, a research assistant at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, Massachusetts, explains that long-term studies of people’s lives and health have shown a significant increase in the risk of dementia, a debilitating brain disease, associated with the consumption of processed red meat.
Dementia currently affects approximately 944,000 people in the UK, a number that experts predict will rise to more than a million by the end of the decade. Alzheimer’s disease, the most common form of dementia, is characterized by a build-up of protein in the brain that leads to memory loss and cognitive decline. Despite extensive research, there is currently no cure for Alzheimer’s or other forms of dementia. However, there are three drugs in trial stages that show promise in slowing the progression of the disease.
Experts stress the importance of dietary choices in mitigating the risk of brain-damaging diseases. The study’s findings suggest that a diet high in nuts, beans, and tofu could serve as a preventive measure, potentially delaying the onset or progression of dementia. This is particularly relevant given the rising prevalence of these conditions and the limited treatment options currently available.
In light of these findings, health professionals recommend that individuals incorporate more plant-based proteins and nutrient-dense foods into their diets. This shift not only supports overall health but also offers a practical approach to reducing the risk of serious neurological diseases.
As research continues, the hope is that greater awareness of the impact of diet on brain health will lead to more informed dietary choices and, ultimately, a reduction in the incidence of brain-damaging diseases.